Home > Specialties > PRK Surgery
PRK Surgery
Photorefractive keratectomy is a type of laser eye surgery, that is used to treat refractive errors, Nearsightedness (myopia), Farsightedness (hyperopia), and Astigmatism) with an excimer laser (A computer-generated, cold laser beam), used to precisely remove and sculpt corneal tissue at the microscopic level). This treatment aims to reduce an individual’s dependency on glasses and contact lenses.
Causes of PRK Surgery
PRK is mainly indicated for the treatment of refractive mistakes of the eye, actually not diseases but conditions that alter the way light focuses on the retina.
The following are specific refractive errors that PRK can treat effectively:
- Myopia (Nearsightedness): PRK works by flattening the cornea to correct myopia so that light focuses correctly on the retina rather than in front of it.
- Hyperopia (Farsightedness): PRK steepens the cornea, which shifts the focus of light onto the retina.
- Astigmatism: PRK reshapes irregularly curved corneas into a spherical configuration to sharpen the focusing of light onto the retina.
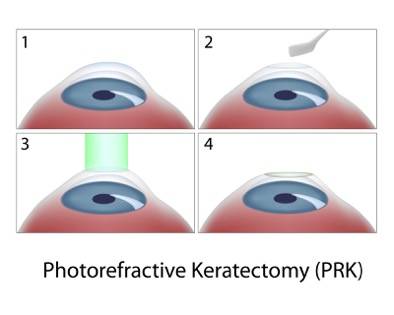
Procedure of PRK
The steps involved in PRK eye surgery (reshaping of the cornea through an excimer laser to correct refractive mistakes like myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism).
The steps of the PRK vision surgery are as follows:
- Pre-Operative Preparation – Before performing PRK surgery, each patient is carefully examined by an ophthalmologist or refractive surgeon to ensure that they are a suitable candidate for his treatment. Such examination includes:
The corneal health, size of the pupil, and measurement of refractive.
Medical History of any previous ophthalmic disorders, past surgical procedures, medications, and systemic diseases to evaluate eligibility for surgery. - Then, the surgeon gives you anesthesia with eye drops on the day of surgery to make the procedure completely painless. Some doctors may also use a mild sedative to relax the patient.
- Epithelial Removal– The epithelium has to be removed; this is the outer layer of the cornea exposing the underlying corneal tissue. There are two common ways of removing the epithelium in PRK: alcohol solution and mechanical brush.
- Laser Reshaping– After the epithelium is removed, an excimer laser is used to reconfigure the curvature of the cornea based on the patient’s precise measurements for refractive error. The high precision of the excimer laser ensures minimal damage to surrounding tissue.
- Immediately after the laser treatment, a temporary soft contact lens or a bandage, much like a therapeutic soft contact lens, is placed over the treated eye, which helps protect the healing cornea and offers comfort. Usually, the bandage contact lens is used for some days until the growth of the epithelium.
- Post-Operative Care – Patients are instructed on postoperative care instructions after PRK eye operation; these include:
Use antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation. Avoid activities like rubbing the eyes. Follow-up appointments with the eye surgeons to monitor healing progress and improvement in visual acuity.
Advantages of PRK Treatments
Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) offers several advantages as a surgical procedure for correcting refractive errors of the eye, compared to other methods like LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis). Here are the key advantages of PRK:
- No flap is created within the cornea during PRK, so the problems associated with creating a flap are avoided.
- This procedure is highly recommended in those patients who have thin corneas or have an improper shape to the cornea for LASIK to be done.
- This helps preserve the strength of the cornea by preventing the creation of flaps and works best for those people who are at risk of having a potential eye trauma.
- No risk of complications related to the flap: Flap dislocation or its inflammation under the flap is avoided.
- Stable results in the long run: Results related to the correction of vision are predictable and stable over long periods.
- Less Risk of Dry Eye Syndrome: Probably less than LASIK, since more of the corneal nerves responsible for tear production will be preserved.
- It is suitable for most patients with various types and degrees of refractive errors.
- This is safer for patients who have certain medical conditions or risky occupations where flap-related complications may become an issue.
- No Risk of Flap-Related Trauma: Because no flap is made, eliminates risks of flap displacement or dislodging.
Modern Eye Care Hospital is a Center of Excellence for Eye Surgeries in Bihar
Address
Mogalkuan – Rahui Road 700m from, Basar Bigha Rd, Sohsarai, Bihar Sharif, Distt Nalanda, Bihar 803118
Call Us
(+91) 9308462602
Mail us
moderneyecare.in@gmail.com
